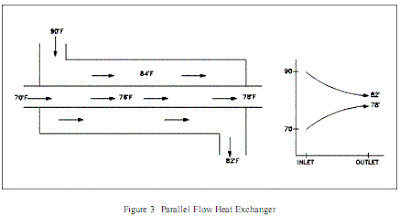
A plate type heat exchanger, as illustrated in Figure 2, consists of plates instead of tubes to separate the hot and cold fluids. The hot and cold fluids alternate between each of the plates. Baffles direct the flow of fluid between plates. Because each of the plates has a very large surface area, the plates provide each of the fluids with an extremely large heat transfer area. Therefore a plate type heat exchanger, as compared to a similarly sized tube and shell heat exchanger, is capable of transferring much more heat. This is due to the larger area the plates provide over tubes. Due to the high heat transfer efficiency of the plates, plate type heat exchangers are usually very small when compared to a tube and shell type heat exchanger with the same heat transfer capacity. Plate type heat exchangers are not widely used because of the inability to reliably seal the large gaskets between each of the plates. Because of this problem, plate type heat exchangers have only been used in small, low pressure applications such as on oil coolers for engines. However, new improvements in gasket design and overall heat exchanger design have allowed some large scale applications of the plate type heat exchanger. As older facilities are upgraded or newly designed facilities are built, large plate type heat exchangers are replacing tube and shell heat exchangers and becoming more common.
 12.26
12.26
 Manusia Biasa
Manusia Biasa
 Posted in
Posted in